Saturated fat often gets a bad reputation, but athletes and anyone looking to keep an active lifestyle, take note: not all fats are created equal! Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are a game-changer for your performance and ability to stay active.
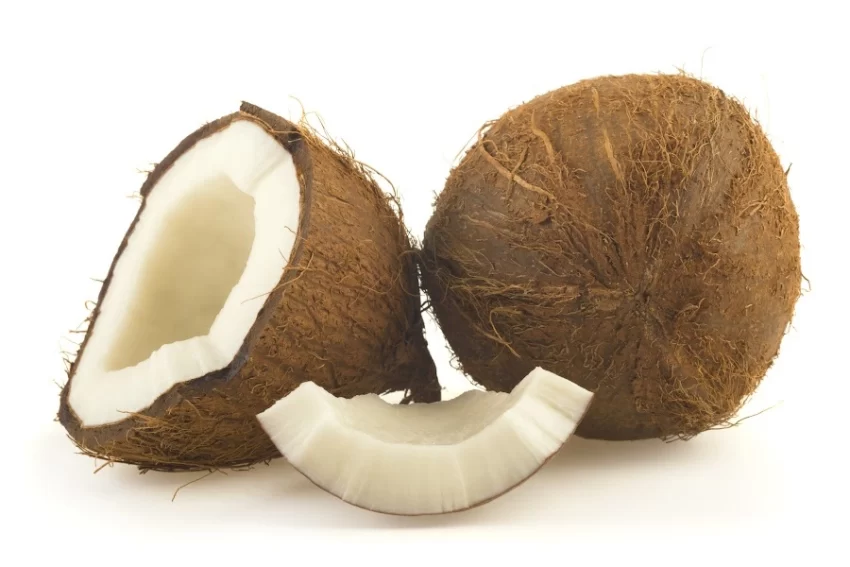
Found in foods like coconut oil, these powerful fats can help fuel your workouts, provide quick energy to your brain, and even support recovery. Think of MCTs as the ultimate training partner for your body and mind!
What Are Medium-Chain Triglycerides?
MCTs are a type of saturated fat composed of six to 12 carbon molecules, making them easier to digest and quicker to metabolize than long-chain triglycerides (LCTs). This unique structure allows MCTs to bypass the typical fat digestion process, delivering energy directly to your cells. Unlike other fats, MCTs are less likely to be stored as fat and more likely to be used as instant fuel.
What are the key types of MCTs?
- Caproic Acid (C6): Quickest to metabolize but has a strong taste.
- Caprylic Acid (C8): Preferred for energy production.
- Capric Acid (C10): Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
- Lauric Acid (C12): Supports immune health and energy metabolism.
Athletic Benefits of MCTs
For athletes, MCTs offer several advantages:
- Instant Energy Boost: MCTs provide a quick source of energy, essential for high-intensity workouts or endurance training.
- Improved Stamina: By sparing glycogen stores, MCTs can help delay fatigue during long training sessions.
- Enhanced Fat Burning: MCTs encourage your body to burn fat as fuel, aiding in weight management and improving body composition. Read more about this topic.
- Cognitive Clarity: MCTs support brain health, helping athletes stay focused and sharp during competition.
- Reduced Muscle Soreness: The anti-inflammatory properties of MCTs may help speed up recovery.
Top Food Sources of MCTs
Incorporating MCT-rich foods into your diet can naturally enhance your performance and overall health:
- Coconut Oil: A well-known MCT source with approximately 60% medium-chain fatty acids. Use it in cooking, baking, or smoothies.
- Palm Kernel Oil: A concentrated source of MCTs, but choose sustainably sourced options.
- Dairy Products: Goat milk, cheese, and butter contain a natural blend of MCTs. Goat milk, in particular, has the highest concentration.
- MCT Oil: A purified supplement derived from coconut or palm oil, ideal for adding to coffee, protein shakes, or salads.
- Grass-Fed Butter: Rich in healthy fats, including MCTs, particularly when sourced from grass-fed cows, great for adding to baked goods, spreading on whole-grain toast, or melting over steamed vegetables.
How to Incorporate MCTs Into Your Diet
Here are some simple ways to add MCTs to your routine:
- Pre-Workout Fuel: Blend MCT oil into your coffee or smoothie for a quick energy boost.
- Post-Workout Recovery: Drizzle coconut oil on roasted vegetables or mix it into oatmeal for a nutritious recovery meal.
- Snacks on the Go: Enjoy cheese sticks or goat milk yogurt for a portable, MCT-packed snack.
- MCT Powder: Use as a creamer for coffee or as an ingredient in protein bars and baked goods.
The Essential Role of MCTs in Ketogenic Diets
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) play a starring role in ketogenic diets, making them a favorite among athletes and wellness enthusiasts following this high-fat, low-carb lifestyle.
MCTs are unique fats that are quickly absorbed and converted into ketones, an alternative energy source for the brain and muscles when carbs are limited. This rapid energy conversion helps boost mental clarity, sustain physical endurance, and support fat-burning goals.
Unlike other fats, MCTs are less likely to be stored as body fat, making them an ideal addition to keto-friendly meals and snacks, whether blended into a morning coffee, drizzled on veggies, or added to protein shakes for a post-workout boost.
MCTs And Disease
Research suggests that MCTs may play a supportive role in managing certain diseases and conditions due to their unique metabolic properties. Here are some examples:
- Neurological Disorders:
MCTs are converted into ketones, which provide an alternative energy source for the brain. This has shown promise in managing conditions like epilepsy, particularly in children following a ketogenic diet. Emerging studies also explore their potential benefits for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, as ketones may support brain function in individuals with impaired glucose metabolism. - Diabetes Management:
MCTs may improve insulin sensitivity and promote better blood sugar control, making them a potential dietary aid for individuals with type 2 diabetes. They can also support weight loss, which is beneficial for managing diabetes. - Fat Malabsorption Disorders:
Because MCTs are more easily absorbed and metabolized than long-chain fats, they can be beneficial for people with conditions like Crohn’s disease, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), or cystic fibrosis, where fat absorption is impaired. - Liver Disease:
In cases of liver dysfunction, MCTs are processed directly in the liver and provide an efficient energy source without requiring complex digestion, making them suitable for individuals with compromised liver function. - Metabolic Disorders:
MCTs may help in managing certain rare metabolic disorders, such as pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency (PDH) or glycogen storage disease, by providing an alternative energy source.
While MCTs show potential for these conditions, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before using them as part of a treatment plan. Further research is needed to fully understand their therapeutic potential and optimal usage for disease management.
Wellness Considerations of MCTs
While MCTs offer many benefits, moderation is key. High doses may cause digestive discomfort, so start with small amounts and gradually increase your intake.
Additionally, while supplements like MCT oil are convenient, whole food sources such as coconut oil and goat milk provide additional nutrients.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs)?
MCTs are saturated fats with 6–12 carbon atoms (C6–C12). Compared with long-chain fats, they are absorbed and metabolized more rapidly, providing a quick source of cellular energy and being less likely to be stored as body fat.
What are the main types of MCTs?
The principal MCTs are caproic acid (C6), caprylic acid (C8), capric acid (C10), and lauric acid (C12). C8 and C10 are commonly used for fast energy production, while C12 also has antimicrobial and immune-supportive properties.
How can MCTs support athletic performance?
MCTs can provide rapid energy, help spare glycogen during longer efforts, support fat oxidation, and may reduce post-exercise soreness due to anti-inflammatory effects. Many athletes use small amounts before or after training for energy and recovery.
Which foods naturally contain MCTs?
Natural sources include coconut oil, palm kernel oil (choose sustainably sourced), dairy products such as goat milk and certain cheeses, grass-fed butter, and purified MCT oil derived from coconut or palm.
Are MCTs useful on a ketogenic diet?
Yes. MCTs are rapidly converted to ketones, which can fuel the brain and muscles when carbohydrate intake is limited. This may support mental clarity, sustained energy, and body-composition goals when used appropriately within a ketogenic plan.
Do MCTs help specific health conditions?
Research suggests supportive roles for epilepsy (as part of ketogenic therapy), cognitive impairment, certain fat-malabsorption conditions, and rare metabolic disorders. Individuals with medical conditions should consult a clinician before using MCT products.
How should I start using MCTs, and are there side effects?
Begin with small amounts (for example, 1 teaspoon per day) to minimize digestive upset, then increase gradually as tolerated. Whole-food sources add additional nutrients; purified MCT oils offer convenience in coffee, smoothies, or post-workout meals.
Summing It Up
Medium-chain triglycerides are a powerful tool for athletes and wellness enthusiasts looking to optimize their performance and overall health. By incorporating MCT-rich foods and supplements into your diet, you can enjoy sustained energy, improved recovery, and enhanced mental clarity.
Fuel your body smarter, perform better, and recover faster with MCTs—nature’s athletic superfood.